Companies are shifting focus from degrees to skills. This new hiring approach prioritizes what candidates can do over where they learned it. Why? Skills predict job performance five times better than education. Yet, 50% of the U.S. workforce - 70 million people - are often overlooked because they lack formal degrees. Skills-based hiring removes this "paper ceiling" by evaluating candidates through coding tests, work samples, and real-world tasks instead of resumes or credentials.
Key insights:
- Degrees are less relevant: Only 13% of college grads are job-ready, and 54% don’t work in their studied field.
- Inclusive hiring: Self-taught developers and bootcamp grads are gaining access to roles.
- Better results: Skills-based hires perform 36% better and stay 9% longer.
This approach benefits companies with faster hiring, better matches, and more diverse teams. It’s not just fair - it’s effective.
What Skills-Based Hiring Replaces
::: @figure 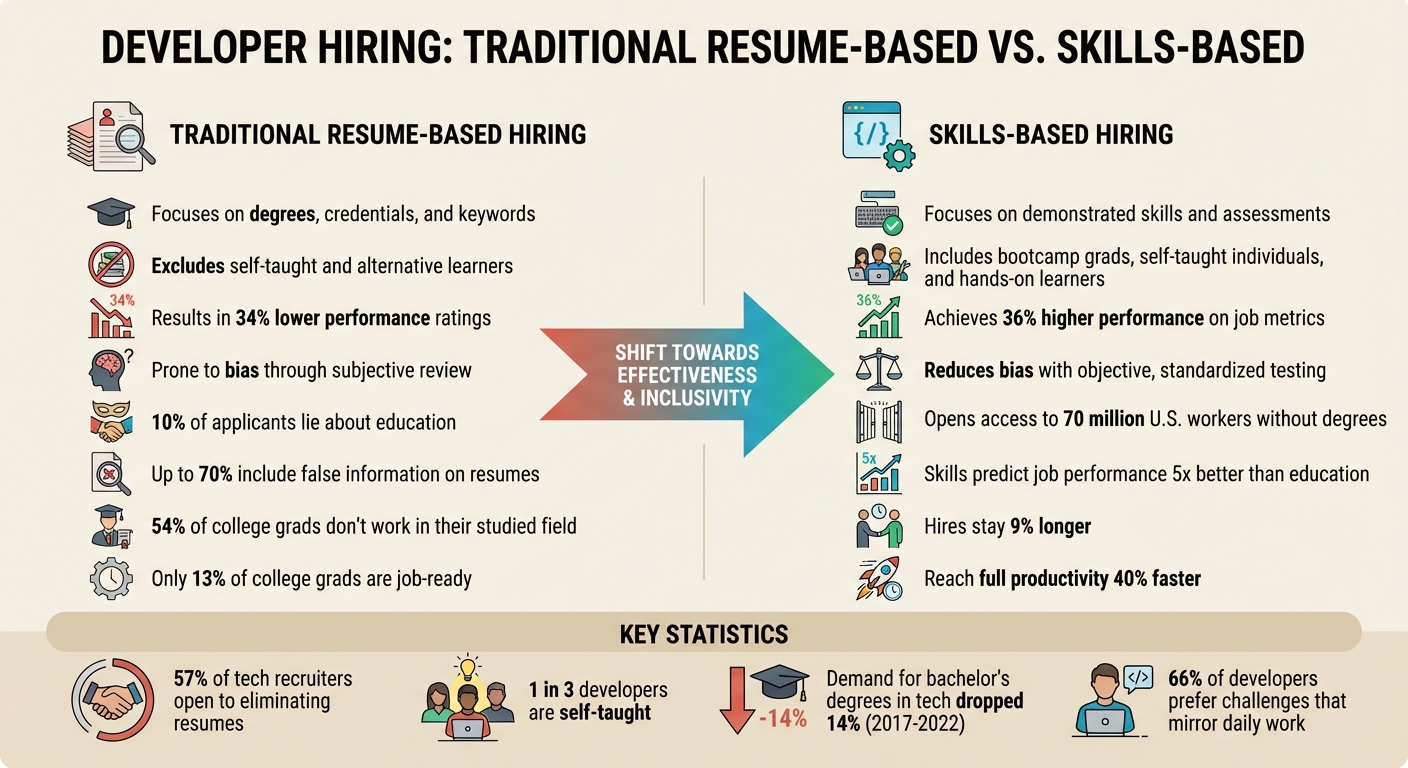 {Traditional vs Skills-Based Hiring: Key Differences and Performance Metrics}
{Traditional vs Skills-Based Hiring: Key Differences and Performance Metrics}
Traditional hiring has long leaned on resumes, but their reliability is questionable. Did you know that 10% of applicants admit to lying about their education ? Even more concerning, up to 70% include false information on their resumes . But the problem isn't just dishonesty - resumes often focus on responsibilities (what someone was supposed to do) rather than competencies (what they can actually do) . This approach prioritizes credentials over true ability, a bias that skills-based hiring aims to eliminate. Instead of relying on degrees or years of experience, companies now emphasize proven technical skills. Resumes are being replaced by work samples like GitHub repositories, portfolios, and coding tests that showcase what candidates can create. Similarly, live coding tests and project-based tasks are taking the place of traditional interview questions, shifting the focus from credentials to capabilities.
Moving from Credentials to Competencies
The "paper ceiling" - a term used to describe barriers faced by skilled workers without formal degrees - affects 70 million U.S. workers who have developed their expertise through bootcamps, self-study, or hands-on experience . This is especially relevant in tech, where 1 in 3 developers are self-taught . Unfortunately, automated applicant tracking systems often filter out these candidates because they lack specific keywords . Adding to this disconnect, 54% of college graduates don't even work in the field they studied, proving that degrees aren't always a reliable measure of job-specific skills .
Companies are starting to address this gap. From 2017 to 2022, the demand for bachelor's degrees in U.S. job postings for computer programmers and scientists dropped by 14% . IBM's Rocket Center facility is a great example of this shift. The company employs workers in cloud computing, cybersecurity, and application development, and nearly one-third of them don’t hold four-year degrees. Joanna Daly, IBM's Vice President of Talent, explains the change in mindset:
"In the past, a manager might have said, 'I need someone with a four-year degree and X years of experience.' Now it's 'I need someone who knows how to code in Java.'" - Joanna Daly, Vice President of Talent, IBM
Work Samples and Assessments Replace Resumes
As companies move away from credential-focused hiring, they are prioritizing tangible work samples over traditional resumes. Developer assessment tools like technical tests, GitHub projects, and real-world tasks now help filter candidates based on their actual skills. This approach ensures that only those with the required abilities advance, regardless of their educational background. Using expert methods to vet technical skills ensures that the evaluation remains objective and focused on job performance. The shift is gaining traction - 57% of tech recruiters are open to eliminating resumes altogether . Plus, employees hired through skills-based methods reach full productivity 40% faster than those hired through resume screening .
GE Digital offers a clear example of this transformation. When staffing a new IT center in Providence, Rhode Island, the company partnered with TechHire Rhode Island to recruit graduates from coding bootcamps. This approach allowed them to fill one-third of their positions with candidates they couldn’t find through traditional hiring methods . Similarly, Goldman Sachs adopted a "skillset recruiting" model, where candidates apply based on their skill areas rather than job titles. Through skill testing, they match applicants to roles that fit their demonstrated abilities .
| Traditional Resume-Based Hiring | Skills-Based Hiring |
|---|---|
| Focuses on degrees, credentials, and keywords | Focuses on demonstrated skills and assessments |
| Excludes self-taught and alternative learners | Includes bootcamp grads, self-taught individuals, and hands-on learners |
| Results in 34% lower performance ratings | Achieves 36% higher performance on job metrics |
| Prone to bias through subjective review | Reduces bias with objective, standardized testing |
This shift isn’t just about creating equal opportunities - it’s about better results. As Vivek Ravisankar, CEO and Co-founder of HackerRank, explains:
"It's hard to figure out how good someone is from a resume. Everyone says they're an expert, but our challenges allow companies to find out who can actually do the job." - Vivek Ravisankar, CEO and Co-founder of HackerRank
How Developer Evaluation Methods Change
The way developers are evaluated has undergone a major transformation, shifting focus from academic credentials to practical skills. Traditional interviews, once centered on abstract puzzles, now emphasize tasks like debugging legacy code, conducting code reviews, or creating API endpoints. These changes reflect real-world developer responsibilities rather than memorized theories from computer science classes .
Modern testing environments closely mimic professional development setups. Candidates now work in browser-based IDEs equipped with features like autocomplete, multi-file support, and integrated version control, making the process feel like their daily work . Assessments also evaluate proficiency with tools like GitHub Copilot, acknowledging the growing importance of AI coding assistants .
Scoring methods have also been revamped. Instead of relying on interviewers' subjective impressions, practical assessments use standardized rubrics to evaluate code correctness, quality, performance, and testing. This approach eliminates unconscious bias and ensures fair evaluation for all candidates. Companies that adopt structured assessments often see a 40% to 60% reduction in interview time, and candidates who pass these tests are 4 to 6 times more likely to receive job offers . These results highlight the effectiveness of realistic, job-relevant assessments.
The benefits of this shift are clear. For instance, Red Hat adopted HackerRank Projects in July 2025 to streamline its hiring process. Their project-based assessments disqualified 63% of candidates in the initial phase due to insufficient skills, cutting live technical interviews by over 60% . Similarly, Outreach used CodeSignal’s platform to automate technical screenings, saving 40% to 60% of senior engineers’ time previously spent on manual interviews .
Practical Assessments Replace Standard Interviews
Coding challenges, take-home projects, and live coding sessions have become the new norm, replacing traditional interviews. According to research, 66% of developers prefer challenges that mirror their daily work . These assessments focus on a candidate's ability to build, debug, and deliver functional code, rather than testing their ability to regurgitate textbook knowledge under pressure.
Take-home projects often involve multi-file repositories, where candidates manage dependencies, write tests, and document their approach. Live coding sessions simulate pair programming, with video and audio allowing interviewers to observe the candidate’s problem-solving process in real time. To ensure these methods remain effective and respectful of candidates’ time, it’s critical to limit take-home projects to 2–4 hours and live coding sessions to 60–90 minutes. Overly lengthy assessments can discourage top candidates from completing the process .
Structured rubrics further enhance fairness and consistency. For example, a backend developer assessment might score candidates on a 1–5 scale across categories like Code Correctness, Code Quality, and Testing. A score of 1 indicates incomplete or buggy solutions, while a 3 reflects functionality for basic cases but failure on edge cases. A 5 represents robust, well-tested code that handles all scenarios gracefully . This standardized framework ensures hiring teams have a shared language for evaluation, removing subjective judgments.
Job Descriptions Focus on Specific Technical Skills
This evolution in hiring has also changed how job descriptions are written. Companies now emphasize specific technical skills rather than vague qualifications. Instead of generic titles like "Senior Software Engineer with 5+ years of experience", job postings now highlight specific frameworks, languages, and tools required for the role. For example, a modern job description might state: "Proficient in Go, strong SQL and PostgreSQL experience, and ability to build and secure RESTful APIs" . This clarity helps candidates self-assess their fit and enables recruiters to target the right talent.
This approach also addresses the "paper ceiling" problem, where candidates without formal degrees are often overlooked. By focusing on what developers can do rather than their educational background, companies are opening doors to self-taught programmers, bootcamp graduates, and career changers. This shift emphasizes technical skills over credentials, helping businesses attract candidates with the right capabilities.
The first step in this process is creating a role competency blueprint. Engineering managers collaborate to separate "must-have" skills from "nice-to-haves", ensuring both job postings and assessments align with the role’s actual demands . For instance, a mid-level backend developer might need proficiency in the primary programming language and strong database experience as must-haves, while familiarity with secondary languages or GraphQL could be considered nice-to-haves. Aligning job descriptions with these technical needs reinforces a practical, skill-focused hiring process that prioritizes demonstrable abilities over traditional qualifications.
Benefits of Skills-Based Hiring for Developers
Skills-based hiring is reshaping how companies evaluate and recruit developers, offering distinct advantages in areas like matching, candidate experience, and team diversity. This approach has proven to enhance performance and retention compared to traditional methods that rely heavily on education-based criteria. These benefits are especially crucial in an industry where 81% of organizations face significant tech skills gaps and 74% struggle to find qualified talent using resume-focused methods.
Better Matching and Faster Hiring
When companies clearly define the technical skills required for a role, they remove much of the guesswork that comes with traditional hiring. Instead of filtering candidates based on degrees or experience alone, skills-based hiring uses role-specific competency frameworks to assess the abilities that truly matter on the job. This ensures that hiring decisions are closely aligned with actual performance needs.
By focusing on these precise requirements, companies can avoid mismatches and prevent applicant tracking systems (ATS) from discarding qualified candidates who lack conventional credentials. This strategy also broadens the talent pool, uncovering skilled professionals from non-traditional pathways - such as the 70 million individuals trained through alternative methods like bootcamps and self-directed learning.
Better Experience for Candidates
Developers strongly prefer hiring processes that mirror the tasks they’ll face in real roles. Skills-based hiring replaces outdated methods like whiteboard questions with practical challenges, such as debugging legacy code or creating API endpoints. These real-world scenarios make the process more relevant, transparent, and fair, allowing candidates to showcase their abilities in a meaningful way.
This approach also reflects an organization’s commitment to growth and internal mobility - qualities that resonate with tech professionals seeking career development opportunities. By reducing reliance on algorithms that prioritize educational credentials, and using AI-driven tools to tailor assessment difficulty in real time, companies create a more personalized and inclusive experience for candidates.
Increased Diversity in Tech Teams
Focusing on skills rather than degrees breaks down the "paper ceiling" that excludes the 50% of U.S. adults without a college degree. This shift is particularly impactful for diversity, as 55% of Latino adults and 61% of Black adults in the U.S. lack a four-year degree, making degree-based hiring a significant barrier. By adopting skills-based practices, companies can expand their talent pool nearly 19 times, welcoming bootcamp graduates, self-taught developers, and career changers who bring fresh perspectives.
For instance, in 2019, BMO launched the BMORE initiative to prioritize transferable skills over traditional banking qualifications. This program led to over 100 hires, including 12 placements from a single event for a role that previously struggled to attract interest. Similarly, Aon has partnered with City Colleges of Chicago since 2017, placing over 300 early-career apprentices into full-time roles by removing degree requirements for entry-level positions.
Teams built through this approach often display enhanced problem-solving abilities. In fact, 76% of CIOs report that diverse teams bring greater creativity to technical challenges. Blind assessments, which hide candidates’ names, demographics, and educational backgrounds, further reduce unconscious bias and ensure a fair evaluation based solely on technical skills. These advantages are transforming tech recruitment and setting a new standard for hiring practices.
Common Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Switching to skills-based hiring might seem straightforward, but it often means grappling with old habits, outdated systems, and real concerns about verifying candidates’ abilities. Even though 94% of employers report that skills-based hires outperform those chosen based on traditional credentials, 72% of organizations still rely on resumes and self-reported skills as their primary tools for evaluation. This disconnect highlights the challenges companies face when trying to bridge the gap between what works and what’s easy to implement. These hurdles are part of the journey toward a hiring approach that prioritizes skills, leading to faster recruitment, better matches, and a more diverse workforce.
Overcoming Resistance to New Methods
For many seasoned recruiters, a four-year degree feels like a safe, familiar benchmark. Shifting away from this mindset isn’t easy, especially when 55% of companies cite time constraints as their biggest obstacle to adopting skills-based practices. Hiring managers also worry about how to validate qualifications without relying on traditional credentials.
"Successful adoption of skills-based hiring involves more than simply stripping language from job postings... firms must overhaul hiring practices, a challenging but necessary step." - Burning Glass Institute and Harvard Business School Researchers
Take Accenture as an example. They tackled resistance with a two-pronged approach: “changing hearts” by sharing apprentices’ personal success stories and “changing minds” by presenting hard data on how skills-based hiring improves outcomes. They also revamped their interview process, allowing managers to directly engage with candidates rather than being handed pre-selected apprentices. Similarly, BMO addressed concerns during its 2019 BMORE initiative by offering tailored onboarding sessions for branch managers. This approach built confidence in hiring non-traditional candidates, leading to over 100 associate banker hires across three states.
Starting small can help. Pilot programs in a single department or for specific roles can demonstrate success before scaling up. Highlighting internal success stories is another way to shift perceptions. For instance, at the University of Chicago Press, senior leaders encouraged hiring managers to distinguish between mandatory and preferred qualifications. This exercise revealed that critical warehouse roles could be filled by skilled local candidates who didn’t have degrees but met all other requirements.
However, addressing resistance is only one piece of the puzzle. The next step is finding tools that effectively measure and validate technical skills.
Selecting the Right Assessment Tools
Once mindsets begin to shift, organizations must ensure their evaluation methods align with a skills-first approach. Without degrees as a fallback, companies need reliable ways to assess technical abilities. The goal is to focus on meaningful signals - like coding ability, problem-solving skills, and design thinking - while avoiding distractions like interview nerves or over-polished presentations. This is especially important since 73% of technical hires show performance discrepancies compared to their initial interview evaluations.
The best tools provide features like browser-based IDEs with autocomplete, syntax highlighting, and testing frameworks. They also include integrity measures, such as proctoring or AI-powered plagiarism detection, to ensure results are authentic. Companies that adopt standardized remote technical assessments report 37% lower hiring costs and a 42% improvement in retention rates.
A two-stage process works well: start with a quick automated screening, followed by a live coding session for top candidates. Keep take-home projects short - no more than 3–4 hours. Calibration sessions, where hiring teams review the same candidate work samples, can also help standardize scoring and minimize bias.
Platforms like daily.dev Recruiter simplify this process. By connecting with developers who are already active in the tech community - reading, contributing, and staying informed - you can skip cold assessments. This approach ensures you’re engaging with candidates who are both skilled and genuinely interested, reducing the workload while maintaining high-quality results.
Strategies and Tools for Skills-Based Assessments
Once internal resistance is addressed, the next step is finding tools that effectively filter out unqualified candidates early while allowing top talent to shine. The ideal approach combines structured methods with automation, ensuring consistency without losing the human element necessary to evaluate problem-solving and communication skills.
Using Structured Interview Frameworks
With the rise of skills-first hiring, structured interview frameworks are becoming essential for fair and consistent candidate evaluations. These frameworks use a standardized set of questions, avoiding the randomness of traditional interviews where one candidate might face system design problems while another gets algorithmic puzzles. Instead, they assess a mix of capabilities like problem-solving, clear communication, practical implementation, and technical design .
Practical tasks that mimic real-world work are now the focus, with structured frameworks formalizing these tasks into repeatable evaluation criteria. Interestingly, 66% of developers prefer practical challenges over theoretical tests because they better reflect the skills needed on the job . For instance, platforms like CoderPad offer collaborative IDEs for live interviews, boasting a 96% candidate completion rate as the tasks feel like real engineering work .
Another effective strategy is using the same code repository across multiple interview rounds, gradually increasing complexity to evaluate how candidates handle evolving requirements . Since 82% of developers incorporate AI tools into their daily workflows , modern assessments should also test how candidates collaborate with AI assistants. CodeSignal's Cosmo feature, for example, evaluates AI-assisted coding to reflect current developer workflows .
Automated Coding Tests and ATS Integration
Automated assessments simplify the initial screening process, saving your engineering team’s time for deeper evaluations. The most efficient tools integrate seamlessly with Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), streamlining the hiring workflow . This is especially important as 68% of recruiters ranked time-to-hire as their top performance metric for 2024 .
One emerging trend is pre-ATS filtering, where short "QuickScreen" tests (lasting 10–15 minutes) are embedded directly into job postings. This approach reduces unqualified candidates early on, saving time and effort. Code Assess AI specializes in this method, focusing on real-world debugging tasks, which helps eliminate up to 70% of candidates who might otherwise clog the pipeline .
For more in-depth evaluations, platforms like HackerRank and CodeSignal offer extensive question libraries and advanced fraud detection. Red Hat, for example, used HackerRank to disqualify 63% of phase-one candidates, cutting live technical interviews by over 60% .
"Partnering with CodeSignal has helped us to manage a very high volume of interest from candidates in our process and quickly assess their technical acumen, without using a ton of engineering hours" - Nadia Abouzaid, Head of Diversity Talent Programs, Asana
Companies using automated assessments typically reduce engineering interview time by 40–60%. Candidates who pass validated technical assessments are also 4–6 times more likely to receive a job offer . To maintain a positive candidate experience, keep initial screenings short (10–15 minutes) and reserve longer tests (30–60 minutes) for later stages . Since over 40% of developers cite unclear hiring processes as a major turnoff, it’s crucial to provide clear expectations about assessment formats and durations upfront .
Integrity measures are equally vital. CodeSignal, for instance, uses tools like "Suspicion Scores", AI-powered plagiarism detection, webcam monitoring, and browser-tab tracking to ensure authentic results . These safeguards are key, considering 73% of technical hires show performance discrepancies compared to their interview evaluations .
Assessment Tool Comparison
Here’s a closer look at some leading assessment platforms, highlighting their key strengths, assessment styles, and ideal use cases:
| Platform | Primary Strength | Assessment Style | Best For | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CodeSignal | Certified assessments by IO psychologists | AI-assisted IDE, fraud detection | High-growth tech teams needing accurate predictions | Enterprise pricing (contact sales) |
| HackerRank | Extensive question library (2,000+), supports 55+ languages | Algorithmic puzzles, AI-powered interviewing | Large enterprises with high hiring volumes | $100–$300/seat annually |
| CoderPad | Live collaborative interviews | Real-time pair programming in browser-based IDE | Assessing communication and problem-solving | Contact sales |
| Code Assess AI | Pre-ATS filtering with short tests | Real-world debugging tasks | Reducing high-volume applicant noise | $49/month (50 assessments) |
| Codility | Strong plagiarism detection and behavioral analysis | Algorithms and analytics | Risk-averse companies prioritizing integrity | Starts at $5,000/year |
Platforms like daily.dev Recruiter take a different route, connecting you with developers already active in the tech community. By engaging with candidates who are reading, contributing, and staying informed, you can skip cold assessments altogether and focus on skilled, genuinely interested applicants. Every introduction is warm, double opt-in, and high-context, reducing wasted time on unqualified candidates.
When selecting an assessment tool, prioritize browser-based IDEs with features like autocomplete, seamless ATS integration, and objective scoring that non-technical recruiters can easily interpret . Keep assessments concise to avoid high drop-off rates, and design them to reflect real job environments. The right mix of structured interviews, automated screening, and developer-focused tools will streamline your hiring process, ensuring you evaluate the skills that truly matter.
Measuring Skills-Based Hiring Results
Key Performance Metrics
Once you've implemented skills-based hiring, it's crucial to monitor specific metrics to measure its impact. The most valuable indicators go beyond just filling positions - they show whether your hires are excelling, staying with the company longer, and adding fresh perspectives to your team. These insights help validate your approach and guide future improvements.
Retention is a standout metric. Companies using skills-based hiring report a 91% boost in retention rates . On average, skills-based hires stay 9% longer than those hired through traditional methods . Additionally, employees without degrees have retention rates that are 10 percentage points higher than their degree-holding counterparts . This is a big deal when you consider the cost of replacing a bad hire for a $60,000 role can range from $7,800 to $22,500 .
Another clear measure of success is diversity. Ninety percent of employers using skills-based hiring see measurable gains in diversity , especially when focusing on candidates from non-traditional backgrounds. Take BMO’s BMORE initiative as an example. Launched in 2019, it prioritized transferable interpersonal skills over formal banking credentials, leading to the hiring of over 100 associate bankers from underinvested communities . Similarly, Walmart removed degree requirements in 2015, and now 75% of its store, club, and supply chain managers - earning an average of $113,000 annually - began their careers as hourly associates .
Efficiency metrics also highlight the benefits of this approach. Companies save between 339 and 660 hours per hire for non-senior roles while cutting cost-to-hire by $1,218 to $2,342 per position when using skills-based assessments . In fact, 81% of organizations report faster time-to-hire, and 90% reduce their mis-hire rates . Tracking these metrics monthly allows you to fine-tune your assessment tools and processes.
Performance outcomes provide even more evidence of the value of skills-based hiring. Employees hired through this method are five times more likely to meet performance standards and only 2% less likely to be promoted compared to traditional hires . These results showcase how focusing on skills rather than credentials can lead to stronger, more capable teams.
Maintaining Relevance Through Skills Mapping
In a world where technology evolves faster than job titles, keeping your hiring criteria up to date is essential. Regular skills mapping ensures your assessments reflect the current needs of your team instead of relying on outdated benchmarks.
Start by breaking down the technical skills required for each role. Avoid vague descriptions like "proficient in JavaScript" and instead specify tasks such as "experience with React hooks, Next.js routing, and TypeScript integration." Aon's apprenticeship program is a great example of this in action. Since 2017, Aon has partnered with City Colleges of Chicago to dissect roles in IT, HR, and finance into specific skills, then worked with educators to create tailored curricula. This approach has led to over 300 apprentices transitioning into full-time roles .
To stay ahead, update your skills inventory regularly - ideally every quarter. With 52% of employers now hiring for AI-related skills , waiting a year to revise your criteria could leave you behind the curve. Pay attention to the skills your top performers use most and adapt your assessments accordingly. For instance, if your team recently adopted AI coding assistants, your hiring process should evaluate candidates’ ability to integrate these tools into their workflows.
Finally, analyze which skills best predict job performance. If debugging proficiency consistently leads to better results than solving algorithmic puzzles, adjust your assessments to emphasize debugging. Use your applicant tracking system (ATS) to compare candidates’ assessment scores with their six-month performance reviews. This data-driven approach ensures you're prioritizing the skills that matter most for success on the job.
Conclusion
Shifting to skills-based hiring changes how companies approach developer recruitment and engagement. Instead of focusing on academic credentials, this method prioritizes actual competencies, leading to better outcomes. By assessing what developers can do rather than where they studied, companies tap into a talent pool that's twice as large, more diverse, and more likely to excel. Research shows that skills-based hires are five times more likely to meet performance standards and tend to stay with companies 9% longer .
This approach requires a fundamental change in recruitment strategies. Job descriptions need to highlight technical skills, and practical assessments should reflect real-world tasks. These changes not only refine the hiring process but also help build stronger, more inclusive teams. As mentioned earlier, this method allows companies to access the 70 million skilled U.S. workers who don’t hold traditional degrees .
Examples from the field underline the effectiveness of this approach. Organizations that have embraced skills-focused hiring have successfully tapped into non-traditional talent pools, leading to noticeable improvements in their recruitment efforts .
daily.dev Recruiter makes this transition seamless by connecting you with active, pre-qualified developers. Every introduction is warm and double opt-in, ensuring you speak only with candidates genuinely interested in your opportunities. By moving away from cold outreach and resume-based screening, you gain access to developers whose skills and interests align with your needs - turning recruitment into a trust-based partnership that benefits both employers and candidates.
FAQs
How does skills-based hiring create more diverse tech teams?
Skills-based hiring focuses on what candidates can do rather than where they went to school or what titles they’ve held. This approach opens doors for many talented individuals who might otherwise be overlooked - like the nearly 50% of U.S. adults without a college degree. By emphasizing proven abilities, companies can access a much broader range of talent, including people with non-traditional career paths.
This hiring strategy also helps reduce unconscious bias. Relying on factors like educational background often unintentionally sidelines underrepresented groups, including women and BIPOC candidates. Shifting the focus to skills ensures opportunities are awarded based on merit and capability, creating a hiring process that’s fairer and more inclusive.
What sets skills-based hiring apart from traditional hiring methods?
Traditional hiring methods often put a heavy emphasis on formal qualifications - things like degrees, job titles, or years of experience. While these factors can provide a snapshot of someone’s background, they don’t always paint the full picture of a person’s abilities. This approach can unintentionally exclude candidates who’ve developed their skills through hands-on experience, self-teaching, or non-traditional paths.
Skills-based hiring takes a different route. Instead of focusing on what’s on paper, this method evaluates candidates based on their actual abilities. Companies might use practical assessments, review portfolios, or assign real-world tasks to gauge whether someone is truly equipped for the role. It’s a more dynamic way to assess talent, especially in industries like tech, where the landscape evolves so quickly.
Shifting the focus to skills rather than credentials doesn’t just make the hiring process more inclusive - it also helps companies tap into a broader, more diverse talent pool. Plus, it ensures new hires are better prepared to meet the demands of today’s fast-changing workplace.
How can companies ensure fair and unbiased skills-based assessments for developers?
To create fair and unbiased skills-based assessments, companies should focus on several key practices. Start by designing evaluations that reflect real-world tasks and emphasize core technical skills. This approach minimizes unconscious bias and ensures all candidates have an equal opportunity to showcase their abilities. Regularly updating assessments is also critical to keep them relevant and to avoid issues like question leaks or over-familiarity.
To maintain the integrity of the process, use anti-cheating measures like randomizing questions and implementing proctoring tools. Standardized, role-specific tests can further ensure that every candidate is evaluated using consistent criteria. By combining these methods, companies can create a hiring process that emphasizes skills over credentials and promotes fairness.


.png)